Corroded Metal: How it Remains an Issue for Buyers Despite Approved Suppliers and What to Do About It
A single corroded metal component can halt production, delay certifications, or trigger costly recalls. For buyers, corrosion is not a minor quality defect. It is a direct threat to cost control, supplier reliability, and brand trust.
Corroded metal is often treated as a downstream manufacturing or design failure. For buyers and procurement leaders, it represents something far more serious. Corrosion impacts product lifespan, warranty exposure, regulatory compliance, brand reputation, and total cost of ownership. When metal components fail prematurely, the root cause often traces back to sourcing decisions, supplier qualification gaps, or material trade-offs made under cost or lead-time pressure.
For buyers operating in regulated or quality-sensitive industries, preventing corroded metal is not about selecting exotic alloys or advanced coatings alone. It is about supplier consistency, material traceability, and validated processes. Smarter supplier and material selection turns corrosion prevention into a proactive procurement responsibility rather than a reactive quality fix.
Understanding Corroded Metal From a Buyer’s Risk Perspective
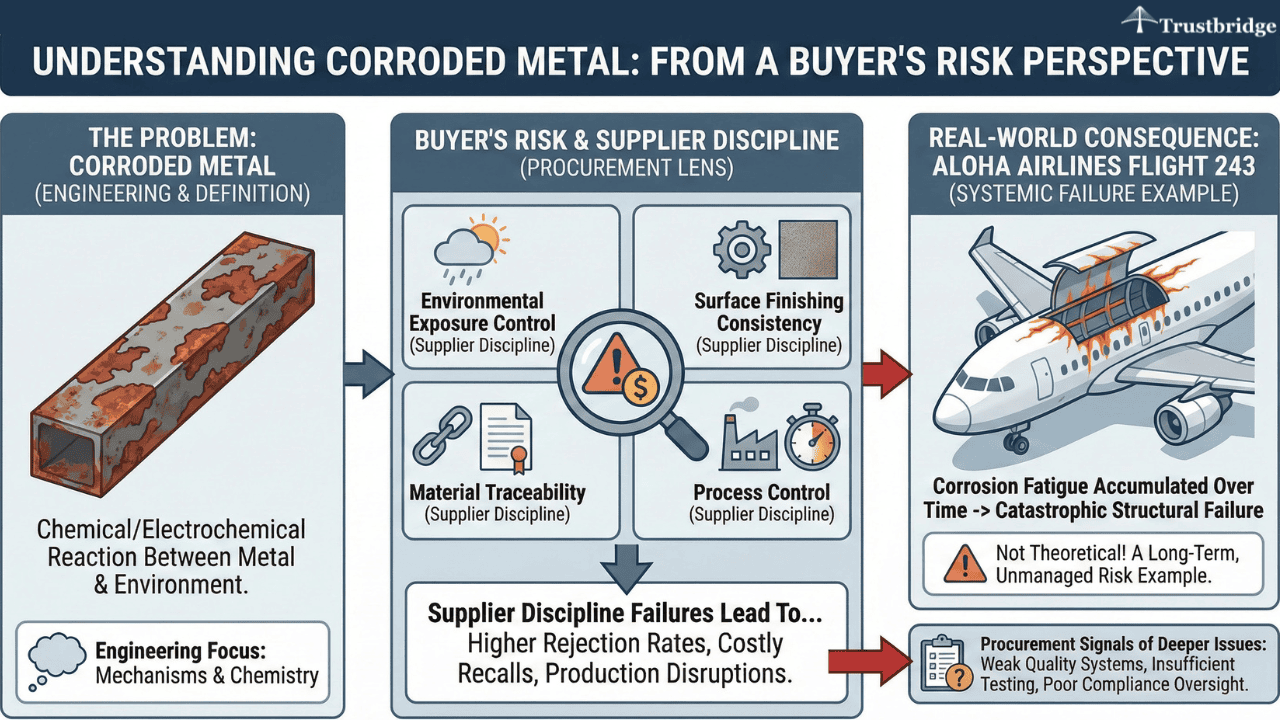
Corroded metal results from chemical or electrochemical reactions between a metal surface and its environment. Engineers may focus on corrosion mechanisms. Buyers must evaluate corrosion as a supplier reliability and supply chain risk. Environmental exposure, surface finishing consistency, material traceability, and process control all depend on supplier discipline.
This risk is not theoretical. In the Aloha Airlines Flight 243 incident, corrosion fatigue accumulated over time and contributed to catastrophic structural failure of an aircraft fuselage. The case remains a widely cited example of how long-term corrosion, when not adequately managed, can escalate into systemic failure.
From a procurement standpoint, corrosion failures often signal deeper issues. These include weak quality systems, insufficient testing protocols, or poor compliance oversight. Buyers who fail to account for these factors during sourcing may face higher rejection rates, costly recalls, or unplanned production disruptions later in the product lifecycle.
Smarter Material Selection Starts With Buyer-Led Decisions
Material selection plays a foundational role in corrosion resistance. Buyers influence this choice more than they often realize. Cost-driven substitutions, limited supplier options, or incomplete material specifications can introduce corrosion risk before production begins.
The Silver Bridge collapse is a classic example of how material selection and long-term environmental exposure can intersect with corrosion risk. Stress corrosion cracking in a critical load-bearing component went undetected, ultimately leading to catastrophic failure.
Aligning Material Requirements With Real-World Operating Conditions
Material specifications must reflect real operating environments, not ideal conditions. Moisture exposure, chemicals, salt, temperature fluctuations, and cleaning agents all accelerate corrosion if overlooked during sourcing. When buyers collaborate early with engineering teams, suppliers are more likely to quote materials that meet real-world performance requirements rather than minimum compliance standards.
Sustainable Sourcing and Long-Term Corrosion Performance
Sustainable sourcing is increasingly tied to corrosion prevention. Materials selected for sustainability credentials must also deliver durability and lifecycle performance. Buyers who align sustainability goals with corrosion resistance reduce premature replacement, waste, and total lifecycle cost.
Vendor Vetting as the First Line of Defense Against Corroded Metal
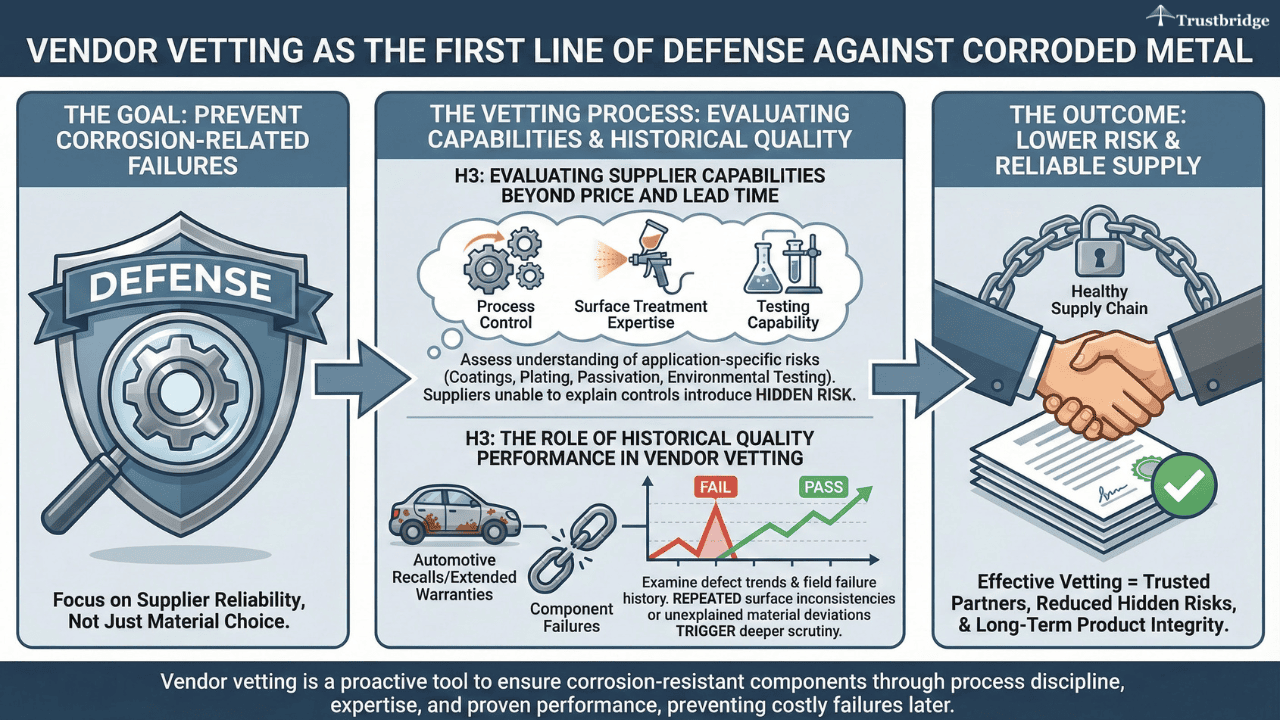
Vendor vetting is one of the most effective tools buyers have to prevent corrosion-related failures. A supplier’s ability to deliver corrosion-resistant components depends on more than material choice alone. Process control, surface treatment expertise, and testing capability are equally critical.
Evaluating Supplier Capabilities Beyond Price and Lead Time
Buyers must assess whether suppliers understand corrosion risks specific to the application. This includes experience with coatings, plating, passivation, and environmental testing. Suppliers unable to clearly explain how they control corrosion variables introduce hidden risk, even if pricing appears competitive.
The Role of Historical Quality Performance in Vendor Vetting
Past performance data provides valuable insight into supplier reliability. Automotive recalls and extended warranties caused by corrosion-related component failures demonstrate why buyers must examine defect trends and field failure history closely.
Suppliers with repeated surface finish inconsistencies or unexplained material deviations should trigger deeper scrutiny during qualification.
Supplier Compliance as a Foundation for Corrosion Prevention
Supplier compliance frameworks such as ISO 13485 and AS9100 play a critical role in preventing corroded metal. These standards enforce disciplined documentation, traceability, and validated processes that directly affect material integrity and surface quality.
Why ISO 13485 and AS9100 Matter to Buyers
Certified suppliers are required to maintain controlled processes for material handling, surface treatment, inspection, and corrective action. For buyers, this reduces variability and ensures corrosion prevention does not rely on undocumented practices. Compliance also improves audit readiness and regulatory confidence across the supply chain.
https://www.iso.org/standard/59752.html
https://www.sae.org/standards/content/as9100d/
Compliance as a Signal of Supplier Maturity
Supplier compliance reflects organizational maturity. Buyers who prioritize certified suppliers reduce corrosion-related surprises during scaling, production transfers, or geographic expansion.
Using Supplier Scorecards to Detect Corrosion Risk Early
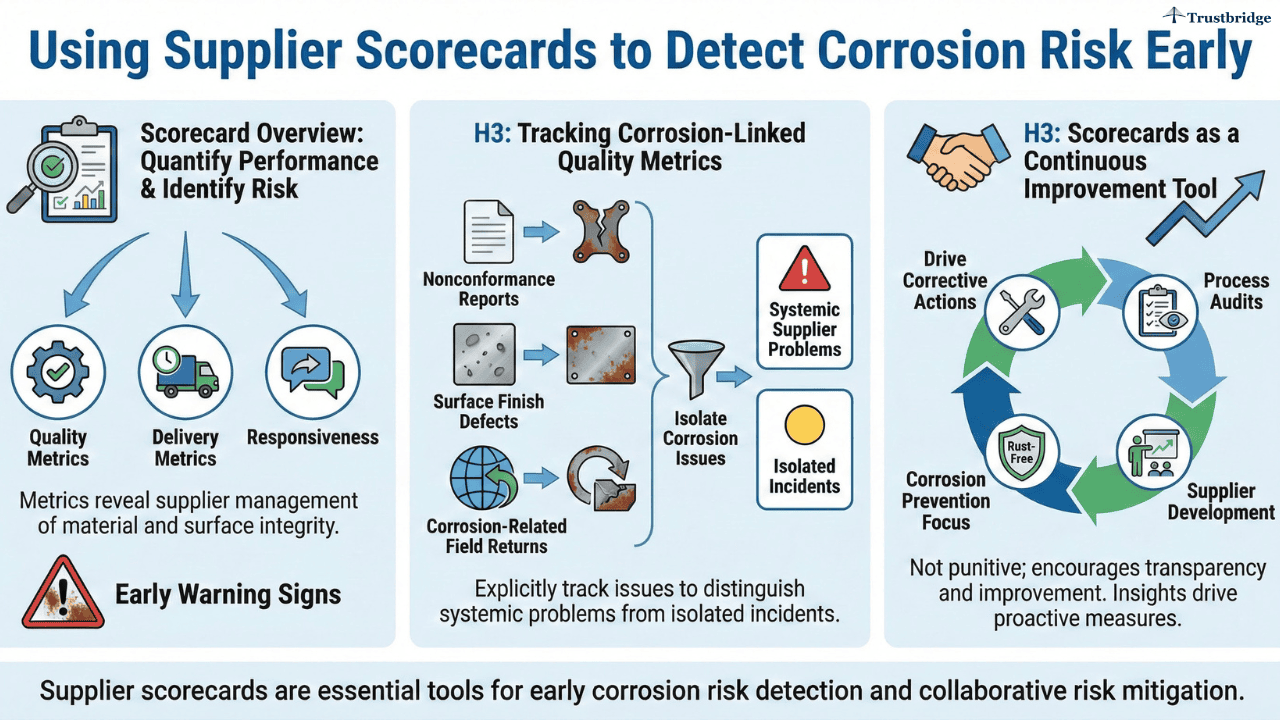
Supplier scorecards allow buyers to quantify performance and identify early warning signs of corrosion-related risk. Metrics tied to quality, delivery, and responsiveness reveal how well suppliers manage material and surface integrity.
Tracking Corrosion-Linked Quality Metrics
Nonconformance reports, surface finish defects, and corrosion-related field returns should be explicitly tracked. Buyers who isolate corrosion-related issues can distinguish between systemic supplier problems and isolated incidents.
Scorecards as a Continuous Improvement Tool
Supplier scorecards should not be punitive. When used correctly, they encourage transparency and improvement. Buyers can use scorecard insights to drive corrective actions, process audits, and supplier development initiatives focused on corrosion prevention.
Supplier Risk Management and the Cost of Corroded Metal
Supplier risk management provides a structured approach to identifying, assessing, and mitigating corrosion-related threats before they affect production or customers. Corroded metal often emerges as a compound risk tied to sourcing decisions, environmental exposure, and inconsistent supplier practices.
The Prudhoe Bay oil spill demonstrates how unmanaged corrosion risk can result in operational shutdowns, regulatory penalties, and long-term reputational damage. Internal corrosion in aging pipelines played a central role in the failure.
Anticipating Environmental and Geographic Risk Factors
Global sourcing increases corrosion risk due to long transit times, humidity exposure, and storage conditions. Buyers must evaluate how suppliers package, store, and ship metal components to prevent degradation before use.
Proactive Risk Mitigation Through Supplier Audits
Regular supplier audits focused on material handling, surface treatment processes, and inspection protocols help buyers uncover corrosion risks early. These audits reduce dependence on final inspection alone and strengthen supplier accountability.
Trustbridge Tip: Preventing corroded metal starts before production, not after. For OEM buyers, the PPAP process is a critical checkpoint to verify material certifications, surface treatments, and process controls that impact corrosion resistance. Treating PPAP as a true approval gate, not a formality, helps buyers reduce downstream failures and supplier risk. Learn what OEM buyers should verify before production release in our blog: What Should OEM Buyers Verify Before Approving a Part for Production Release?
Why Buyers Must Own Corrosion Prevention Strategy
Corroded metal is rarely the result of a single poor decision. It is often the cumulative outcome of sourcing shortcuts, insufficient vetting, weak compliance enforcement, or incomplete risk assessment. Buyers sit at the intersection of cost, quality, compliance, and supplier relationships.
By taking ownership of corrosion prevention, buyers move from reactive problem-solving to proactive risk management. This shift protects product reliability, strengthens supplier partnerships, and improves long-term procurement performance.
Conclusion: Smarter Buyer Decisions Create Corrosion-Resistant Supply Chains
Preventing corroded metal is not solely an engineering challenge. It is a strategic procurement responsibility that begins with smarter supplier and material selection. Buyers who prioritize sustainable sourcing, rigorous vendor vetting, strong supplier compliance, data-driven supplier scorecards, and proactive supplier risk management significantly reduce corrosion-related failures across the product lifecycle.
When buyers treat corrosion as a sourcing and supplier quality issue rather than a downstream defect, they create more resilient supply chains, lower total costs, and deliver greater value to their organizations.
Build a Corrosion-Resistant Supplier Network
If corroded metal is impacting your product quality, supplier performance, or procurement KPIs, it is time to reassess how you qualify and manage suppliers. Adopt a buyer-first supplier evaluation and risk management approach to source corrosion-resistant components with confidence. Strengthen your supplier network today and turn corrosion prevention into a measurable procurement advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why does corroded metal still occur even when buyers work with approved suppliers?
Approved suppliers can still introduce corrosion risk if material controls, surface treatments, or environmental handling are not consistently managed. Corrosion often stems from undocumented material substitutions, weak process controls, or gaps in supplier oversight during repeat production.
2. How much influence do buyers actually have over preventing corroded metal?
Buyers play a direct role in corrosion prevention through supplier selection, material approval, compliance requirements, and ongoing performance monitoring. Vendor vetting, PPAP approvals, and supplier scorecards all determine how well corrosion risk is controlled over time.
3. How does supplier compliance help reduce corrosion-related failures?
Supplier compliance frameworks such as ISO 13485 and AS9100 require documented controls for material handling, surface treatment, inspection, and corrective action. These controls reduce variability and ensure corrosion prevention practices are applied consistently across production runs.
4. What is the most important takeaway for buyers trying to prevent corroded metal?
Corroded metal is rarely caused by a single failure. It is usually the result of sourcing shortcuts, insufficient supplier vetting, weak compliance enforcement, or incomplete risk assessment. Buyers who treat corrosion as a procurement and supplier management issue can prevent failures before they impact production or customers.


