Low-Volume Injection Molding: A Cost-Effective Solution for Prototyping & Small Batches
Low volume injection molding has become a go-to manufacturing strategy for buyers and OEM procurement teams seeking a scalable and reliable alternative to traditional high-volume tooling. Consider a common scenario: an OEM preparing to launch a new enclosure for an industrial device needs 500 parts to complete validation, regulatory testing, and early customer pilots. Committing to hardened steel tooling and mass-production minimums at this stage would lock capital too early and delay timelines. Low volume injection molding allows buyers to move forward without the long lead times and heavy upfront tooling commitments associated with conventional production methods.
For procurement managers and sourcing leads, the value of low volume injection molding lies in its ability to support iterative design validation, supply chain readiness checks, and early market entry while reducing risks such as late-stage tooling changes or supplier requalification. This manufacturing approach enables buyers to source parts that closely match final production materials and performance requirements, while maintaining control over dimensional quality, material traceability, and supplier accountability. As supply chains grow more complex and programs face tighter launch windows, low volume injection molding provides buyers with a practical way to accelerate development without compromising compliance or operational credibility.
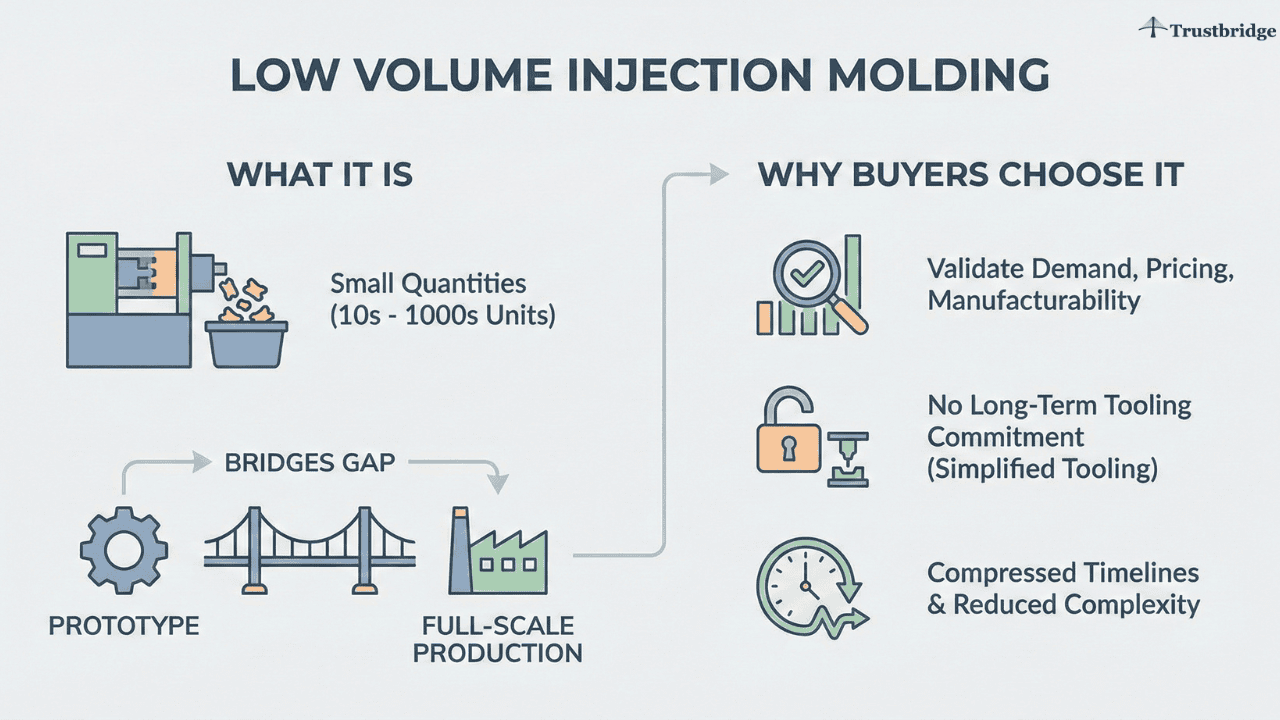
What Low Volume Injection Molding Is and Why Buyers Choose It
Low volume injection molding refers to producing molded components in relatively small quantities, typically ranging from tens to several thousand units. Commercially, this range is significant because it bridges the gap between one-off prototypes and full-scale production, allowing buyers to validate demand, pricing, and manufacturability before committing to long-term tooling. Instead of relying on hardened steel molds designed for millions of cycles, this approach uses simplified or softer tooling and flexible manufacturing setups that reduce setup complexity and compress timelines.
Buyers often choose low volume injection molding over CNC machining or 3D printing for plastic parts when they need production-representative materials, tighter tolerances, and surface finishes that match final specifications. While 3D printing and CNC machining serve early concept validation well, they fall short when parts must behave like true production components. Low volume injection molding delivers parts that closely replicate the appearance, mechanical properties, and dimensional accuracy of full-scale production components. This allows procurement teams to lock material choices, validate tooling strategies, and confirm supplier capability earlier—reducing the likelihood of costly supplier switches or tooling rework later in the program.
How Low Volume Injection Molding Supports OEM Manufacturing
Low volume injection molding aligns closely with the goals of OEM manufacturing teams that must balance speed, quality, and cost against fixed launch milestones. Manufacturing engineers and commodity managers benefit from validating designs, materials, and supplier processes under real production conditions without committing to high-volume production contracts too early in the program timeline.
This capability is especially valuable when designs are still evolving or when regulatory and certification approvals must be secured before scaling. Because low volume molded parts are produced using production-grade materials and controlled molding processes, teams can confidently use them for mechanical testing, thermal cycling, fit-and-function checks, and early field or customer trials. This directly reduces risks such as failed validation tests, late design freezes, or post-launch quality escapes as programs transition toward full production and commercialization.
Integrating Low Volume Injection Molding Into the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP)
The production part approval process (PPAP) plays a critical role in confirming that parts meet design and quality requirements before full-scale manufacturing begins. When PPAP activities stall, launch timelines slip and downstream production readiness is compromised. Low volume injection molding accelerates PPAP by enabling buyers to obtain production-representative parts earlier in the lifecycle, often during pilot or bridge production phases.
Compared to alternatives like 3D printing or CNC machining, molded parts allow quality engineers and supplier quality teams to complete dimensional layouts, capability studies, and functional validation using parts made under real molding conditions. This earlier access helps sourcing managers and quality leads surface tooling or process risks while there is still time to correct them strengthening launch confidence and improving production readiness.
Because parts are molded with consistent materials and controlled parameters, procurement and quality teams can complete validation activities more efficiently and with greater confidence. This is most impactful during late prototype and early pilot stages, when changes are still manageable but timelines are tightening.
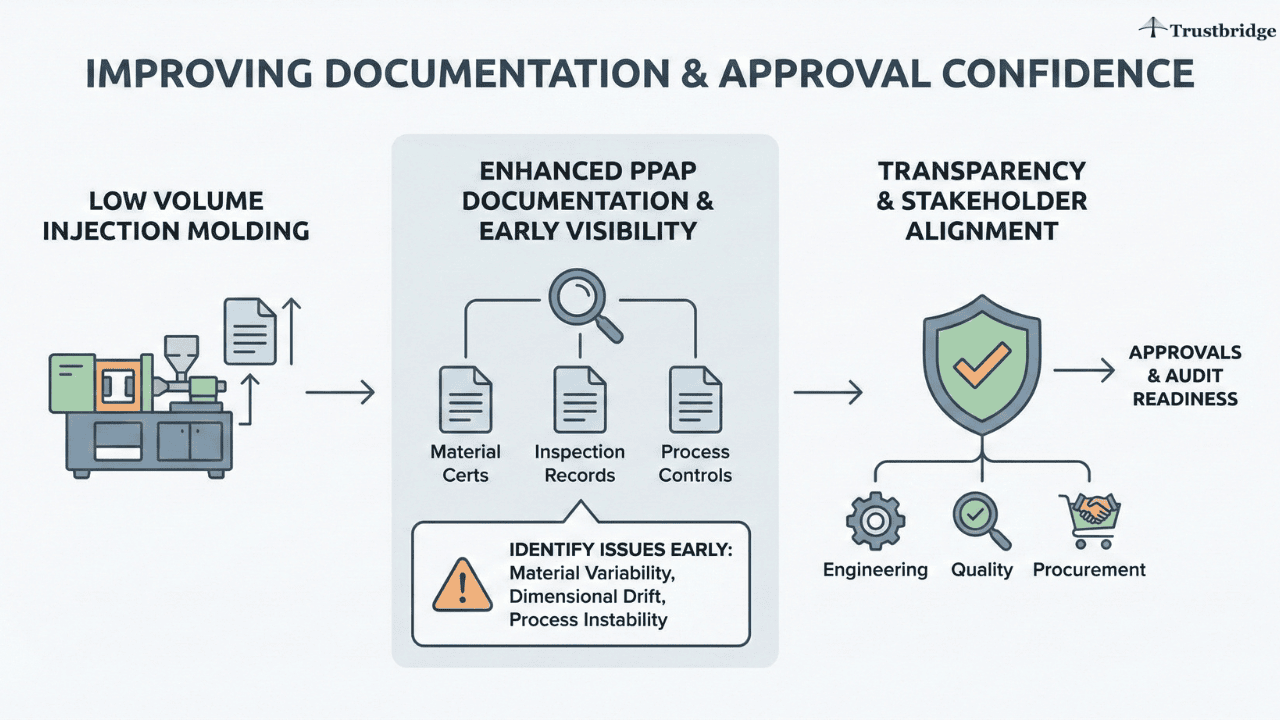
Improving Documentation and Approval Confidence
Low volume injection molding also improves documentation quality and traceability throughout PPAP. Buyers gain early visibility into material certifications, inspection records, and process controls that mirror those required for full production. This helps teams identify issues such as material variability, dimensional drift, or process instability before they escalate into launch delays.
The resulting transparency strengthens internal approvals and audit readiness, ensuring that engineering, quality, and procurement stakeholders are aligned on supplier capability well before volume production begins.
Vendor Vetting and Supplier Compliance in Low Volume Injection Molding
Vendor vetting typically occurs during pre-PPAP, pilot, or bridge production phases, making low volume injection molding an ideal evaluation window. Selecting the right supplier at this stage ensures that early-stage parts meet quality expectations and that the supplier can scale responsibly as volumes increase. Buyers must assess tooling expertise, mold ownership models, process controls, and mold maintenance practices when evaluating partners.
Suppliers with proven experience in small batch molding, material consistency, and tight tolerances demonstrate better repeatability across batches. For buyers, this translates into fewer quality escapes, reduced rework, and a lower risk of supplier transitions as programs mature.
Maintaining Supplier Compliance Over Time
Once a supplier is approved, compliance becomes an ongoing monitoring effort rather than a one-time checkpoint. Compliance spans dimensional accuracy, material conformity, documentation discipline, and adherence to industry or regulatory standards. Maintaining this consistency during low volume runs ensures continuity as programs move toward higher volumes.
For buyers, continuous compliance monitoring prevents program disruptions, protects against liability exposure, and supports uninterrupted production ramp-ups as demand increases.
Supplier Lead Time Reduction Through Low Volume Injection Molding
One of the most compelling advantages of low volume injection molding is supplier lead time reduction. Compared to traditional tooling approaches that may take months, simplified tooling and faster mold modifications allow suppliers to respond in weeks. This agility enables procurement teams to accommodate design revisions, incorporate customer feedback, or adjust schedules without derailing launch plans.
Shorter lead times also reduce inventory risks associated with overbuilding or inaccurate forecasts. Buyers can align deliveries more closely with actual demand, maintaining flexibility even when market conditions or program requirements shift unexpectedly.
Cost Efficiency and Total Value for Buyers
Low volume injection molding delivers cost efficiency across process, design, and supplier dimensions. Faster validation cycles reduce engineering hours, fewer late-stage design changes limit scrap, and early supplier validation prevents costly requalification efforts during scale-up. Instead of restarting sourcing efforts, buyers transition smoothly into higher volumes with established suppliers and validated tooling.
Viewed through a total cost of ownership lens, this approach improves internal metrics such as launch adherence, quality incident rates, and supplier stability—directly supporting predictable program outcomes and faster revenue realization.
Trustbridge Tip: Low-volume injection molding helps buyers validate materials, processes, and supplier controls early, but corrosion risks are often missed because upstream handling, storage, or finishing conditions are not scrutinized during early runs. Buyers should use these early production phases to identify root-cause exposure points and strengthen supplier audits before scale. To understand why corrosion persists despite approved vendors and how buyers can build earlier awareness, read our blog: Why Do Buyers Still Face Corroded Metal Failures Despite Using Approved Suppliers?
Strategic Advantages of Low Volume Injection Molding for Buyers
Strategically, low volume injection molding de-risks product launches by addressing tooling, quality, and supplier performance risks early. Buyers gain measurable insights into supplier responsiveness, process capability, and communication effectiveness under real manufacturing conditions.
This early validation enables stronger commercial negotiations, clearer capacity planning, and more reliable sourcing strategies as programs scale. The result is a smoother transition from prototyping to full production with fewer surprises and stronger long-term supplier alignment.
Conclusion
Low volume injection molding is a powerful tool for buyers seeking flexible solutions for prototyping and small batch production. By reducing risk, improving speed, and maintaining control across supplier validation and approval processes, it delivers meaningful operational and strategic value. For procurement teams navigating tight timelines and complex supply chains, this approach provides a confident path from early development to scalable production.
If you are sourcing parts for prototyping or early production, evaluate suppliers based on tooling capability, material traceability, and process control maturity. Using low volume injection molding strategically can accelerate approvals, reduce lead times, and set the foundation for a stable production ramp.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is low volume injection molding, and when should buyers consider it?
Low volume injection molding is used to produce small quantities of molded parts using production-grade materials and processes. Buyers typically consider it during prototyping, pilot builds, or early production when designs are still being validated and committing to high-volume tooling would increase cost and risk.
2. How does low volume injection molding support OEM manufacturing programs?
For OEM manufacturing, low volume injection molding allows buyers to validate part performance, materials, and supplier capability under real production conditions. This ensures early parts closely match final production requirements, reducing surprises during scale-up and improving overall program readiness.
3. Can low volume injection molding be used for the production part approval process (PPAP)?
Yes, low volume injection molding is well-suited for PPAP activities. Because parts are produced using controlled processes and production-intent materials, buyers can complete dimensional inspections, functional testing, and documentation earlier, accelerating approvals and reducing delays before full production.


